m1ts0s
News poster
- Μηνύματα
- 2.337
- Reaction score
- 3.650
http://diracdocs.com/ISEAT15_Brannmark_Sternad.pdf
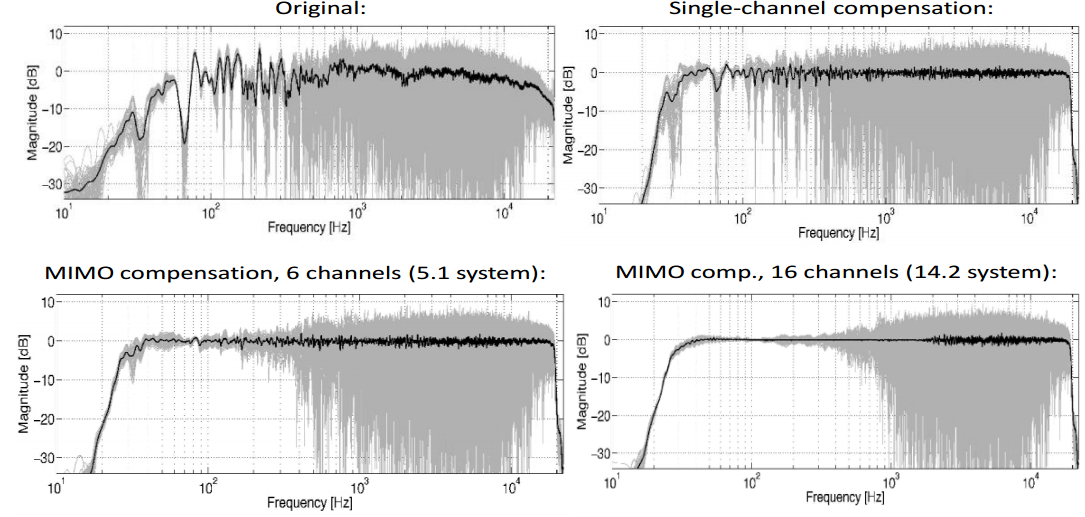
Καλό overview του τι κάνει η Dirac:
"The discussion above leads to several possible alternatives for the design of precompensation filters. Let us summarize their properties and compare the performances of some of them.
Single-point methods, which take the response at only one design point in space into account, are non-robust. They will not be considered further below.
Minimum phase multipoint design: We may represent the average response at a set of design points by an average frequency domain function, such as the black line in the upper part of Figure 2. We can then construct the corresponding minimum phase impulse response (as in the lower part of Figure 4 and the upper left part of Figure 6). We then invert it by using its causal and stable inverse filter (illustrated by the upper right-hand part of figure 6.) Such a design will be good in an average sense in the frequency domain. The resulting design uses no modeling delay so the compensated impulse response will have no pre-ringings. However, other time-domain properties are not targeted and remaining post-ringings in the impulse responses may be substantial.
Unconstrained mixed phase multipoint design (a noncausal Wiener solution). This solution takes the MSEs at all control points into account and minimizes a weighed average of them. This generates a noncausal precompensator that therefore requires the use of a very large modeling delay. The resulting performance is often good in an average sense in the frequency domain, but this design does not care about how the remaining errors are distributed over time in the compensated impulse responses.
Constrained, robust mixed phase multipoint design. This solution takes the MSEs at all control points into account and minimizes a weighted average of them under constraints. The constraints may include constraints on loudspeaker powers at different frequencies, a constrained modeling delay and constraints on the allowable pre-ringings of the compensated impulse responses at all control points in the targeted area [1]. The resulting compensators are stable and causal IIR filters, with as long impulse responses as needed. The performance of this strategy is good in an average sense in the frequency domain, and it also corrects time-domain properties. It provides a slightly worse MSE than an unconstrained Wiener solution, but the sound quality is much better from a psychoacoustic perspective."
Καλό overview του τι κάνει η Dirac:
"The discussion above leads to several possible alternatives for the design of precompensation filters. Let us summarize their properties and compare the performances of some of them.
Single-point methods, which take the response at only one design point in space into account, are non-robust. They will not be considered further below.
Minimum phase multipoint design: We may represent the average response at a set of design points by an average frequency domain function, such as the black line in the upper part of Figure 2. We can then construct the corresponding minimum phase impulse response (as in the lower part of Figure 4 and the upper left part of Figure 6). We then invert it by using its causal and stable inverse filter (illustrated by the upper right-hand part of figure 6.) Such a design will be good in an average sense in the frequency domain. The resulting design uses no modeling delay so the compensated impulse response will have no pre-ringings. However, other time-domain properties are not targeted and remaining post-ringings in the impulse responses may be substantial.
Unconstrained mixed phase multipoint design (a noncausal Wiener solution). This solution takes the MSEs at all control points into account and minimizes a weighed average of them. This generates a noncausal precompensator that therefore requires the use of a very large modeling delay. The resulting performance is often good in an average sense in the frequency domain, but this design does not care about how the remaining errors are distributed over time in the compensated impulse responses.
Constrained, robust mixed phase multipoint design. This solution takes the MSEs at all control points into account and minimizes a weighted average of them under constraints. The constraints may include constraints on loudspeaker powers at different frequencies, a constrained modeling delay and constraints on the allowable pre-ringings of the compensated impulse responses at all control points in the targeted area [1]. The resulting compensators are stable and causal IIR filters, with as long impulse responses as needed. The performance of this strategy is good in an average sense in the frequency domain, and it also corrects time-domain properties. It provides a slightly worse MSE than an unconstrained Wiener solution, but the sound quality is much better from a psychoacoustic perspective."

